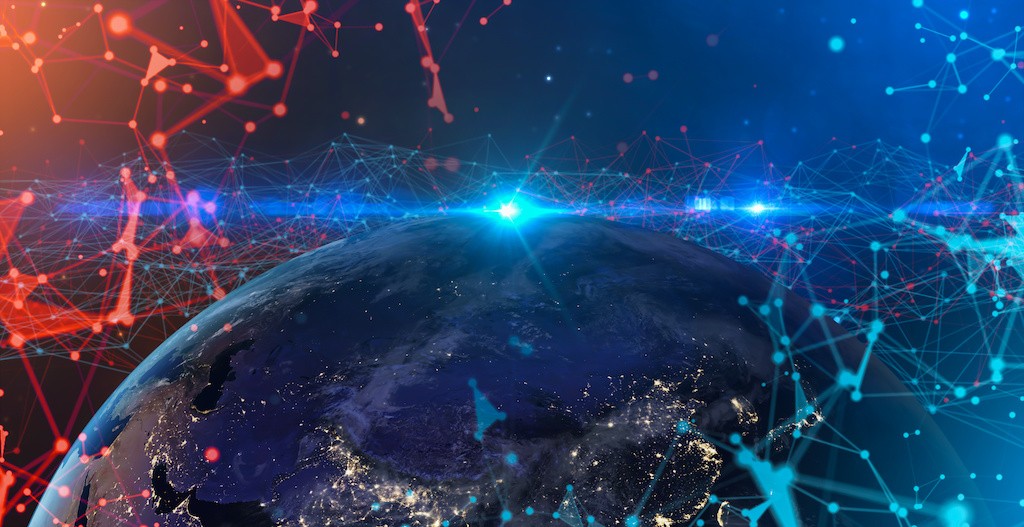
As telecom infrastructure evolves, scalable and energy-efficient connectivity remains a challenge—especially for large IoT ecosystems. LoRa technology, known for its long-range, low-power design, offers a unique solution. With increasing demand for decentralized systems, integrating LoRa with edge AI and blockchain-driven models is becoming vital. This convergence empowers smart environments—from urban grids to industrial sensors—to operate autonomously, efficiently, and in real time.
In decentralized AI networks, communication must be fast, reliable, and power-conscious. LoRa fits that requirement. By enabling devices to interact directly at the edge, it eliminates the need for costly centralized control. This capability positions LoRa as a critical enabler for the future of smart telecom.
LoRa Technology in Telecom’s IoT Evolution
Telecom operators face growing pressure to support massive IoT deployments without overloading existing infrastructure. LoRa, a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) protocol, delivers reliable connectivity over several kilometers using minimal energy. It operates in unlicensed sub-GHz bands, allowing providers to deploy networks with reduced regulatory barriers and lower costs.
Because of its adaptability, LoRaWAN supports various use cases—from logistics and agriculture to urban infrastructure. It uses adaptive data rates, bidirectional messaging, and flexible payloads. These features allow telecom networks to scale intelligently across diverse operational environments.
Decentralized Intelligence at the Network Edge
Today’s networks require more than raw connectivity—they need embedded intelligence. In LoRa-based systems, distributed machine learning and deep neural networks enable smart communication between devices and gateways. These edge nodes process data locally, lowering latency and easing the load on centralized servers.
Using clustering algorithms like K-means and DBSCAN, LoRa networks dynamically assign transmission settings such as spreading factor and data rate. This optimization reduces interference and maintains consistent performance. It also makes networks self-adjusting and highly resilient—especially important for telecom use in industrial and urban areas.
LoRa’s Role in Supporting AI-Driven Mesh Networks
LoRa’s decentralized model transforms wireless architecture. Devices don’t just transmit—they collaborate. In mesh networks, each LoRa node interacts with its neighbors, reroutes data as needed, and responds to changing conditions. This setup offers redundancy, broader coverage, and stronger fault tolerance.
For telecom providers, this means more robust connectivity in hard-to-reach locations. It also enables applications like real-time EV charging station monitoring or environmental data collection. LoRa’s energy efficiency further enhances sustainability—a key priority for modern telecom strategies.
The Future of Telecom with LoRa and Edge AI
Looking forward, LoRa will play a central role in telecom’s shift to edge-based, intelligent infrastructure. In smart cities, LoRa sensors already feed AI systems that manage traffic, energy, and pollution in real time. These decentralized networks reduce both cost and complexity by minimizing reliance on central data centers.
Meanwhile, low-resource AI training methods such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) are making it easier to deploy powerful models at the edge. When combined with LoRa networks, these tools enable dynamic, context-aware systems that adapt instantly to their environment.
As AI and IoT continue to converge, telecom operators that embrace LoRa will be better positioned to build scalable, efficient, and autonomous networks.